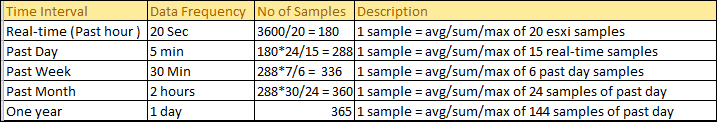
ESXi Management agent can be restarted in couple of ways
will restart all the management agents, hostd, ntpd, sfcbd, slpd, wsman, vodb
Method 2 :
Run following commands,
Method 3 :
If Automatic Startup/shutdown is enabled on VMs , virtual machine may restart.
DUCI
- Connect to ESXi Host
- Press F2 , provide the credentials ( Login using root)
- Go to Trouble shooting , Navigate to Restart ,Management Agents
Local Console or ssh
Method 1 : No Down time to VMs- /sbin/services.sh restart
will restart all the management agents, hostd, ntpd, sfcbd, slpd, wsman, vodb
Method 2 :
Run following commands,
- /etc/init.d/hostd restart
- /etc/init.d/vpxa restart
Method 3 :
- service mgmt-vmware restart
- service vmware-vpxa rest
If Automatic Startup/shutdown is enabled on VMs , virtual machine may restart.